Battery Regulation - 2023/1542
In July 2023, the European Union approved a new battery regulation known as Regulation 2023/1542.
The primary aim of this regulation is to create a harmonized legislation for the sustainability and safety of batteries.
Here are some key points from the new regulation:
- Sustainability and Safety: The regulation focuses on ensuring that batteries are sourced, manufactured, and used in a sustainable manner.
- Global Impact: Given the strategic importance of batteries, the regulation aims to provide legal certainty to all operators involved and prevent discrimination, trade barriers, and market distortions. It recognizes batteries as crucial for sustainable development, green mobility, clean energy, and climate neutrality.
- Life Cycle Approach: The regulation covers the entire life cycle of batteries placed on the market in the EU. This includes rules related to their production, use, recycling, and disposal.
- Transition to Electromobility: As part of the European Green Deal, the regulation supports the transition from fossil fuels to electromobility. It encourages the use of batteries in electric road transport vehicles and other means of clean transportation.
- Stricter Requirements: Battery manufacturers will be subject to stricter environmental and due diligence requirements if they want to sell batteries in the European market.
- CE Marking:
Manufacturers will be required to affix the CE marking to batteries before placing them on the market or putting them into service, starting from August 18, 2024. Notified bodies need to be involved in granting the CE marking for certain types of batteries.
DNV is in process to become a notified body for the New battery regulation.
The sustainability requirements outlined in Regulation 2023/1542 focus on ensuring that batteries are sourced, manufactured, and used in an environmentally responsible manner. Here are some key aspects:
- Ecodesign and Energy Efficiency: The regulation encourages the design of batteries with improved energy efficiency and reduced environmental impact.
- Material Sourcing: Battery manufacturers are expected to use sustainable materials and minimize hazardous substances. For example, materials; lithium, cobalt, nickel.
- Recycling and Second Life: The regulation emphasizes recycling and reuse. Manufacturers must design batteries for easy disassembly and recycling.
- Carbon Footprint: Manufacturers are encouraged to reduce the carbon footprint associated with battery production.
- Labeling and Information: Batteries placed on the market must be labeled with relevant information, including their environmental impact, recycling instructions, and energy efficiency ratings.
- Collection and Disposal: The regulation promotes efficient collection and safe disposal of used batteries.
Explore the key milestones for batteries below. For certain products the timelines can differentiate slightly, for more details reach out to DNV.
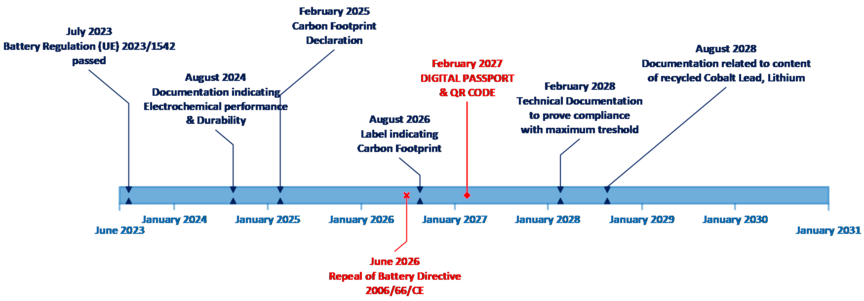
Do you want to have further guidance? We have also developed specific workshops to assist you in your compliance journey.




